IAP 2024 Day 2 - Intro to React
Why I change the course?
As the course has added more content and the quality of audio is as good as the 2021 version.
What React does?
A JavaScript library for building user interfaces.
Components
What is a <component /> really?
Fake HTMl Tag -> Abstraction for a bunch of HTML, CSS, and Javascript in one file
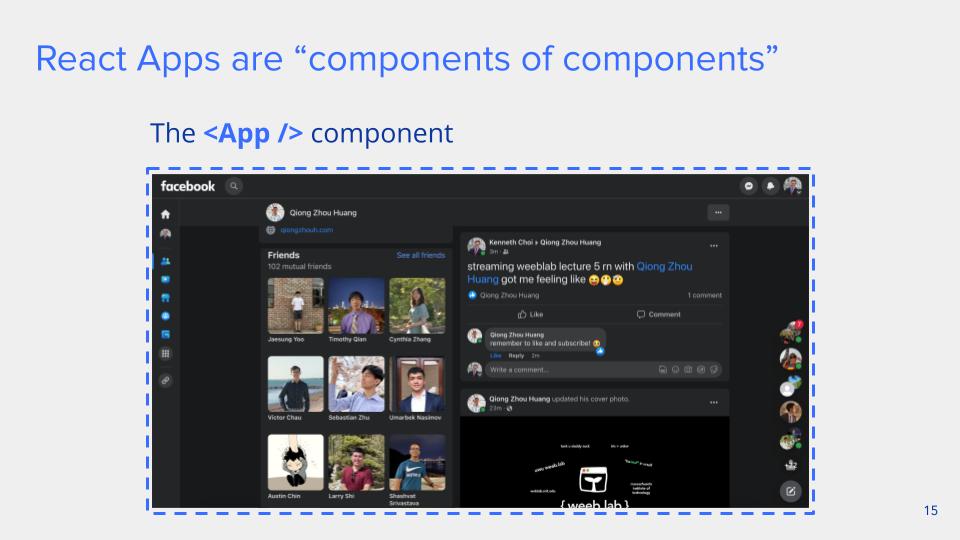
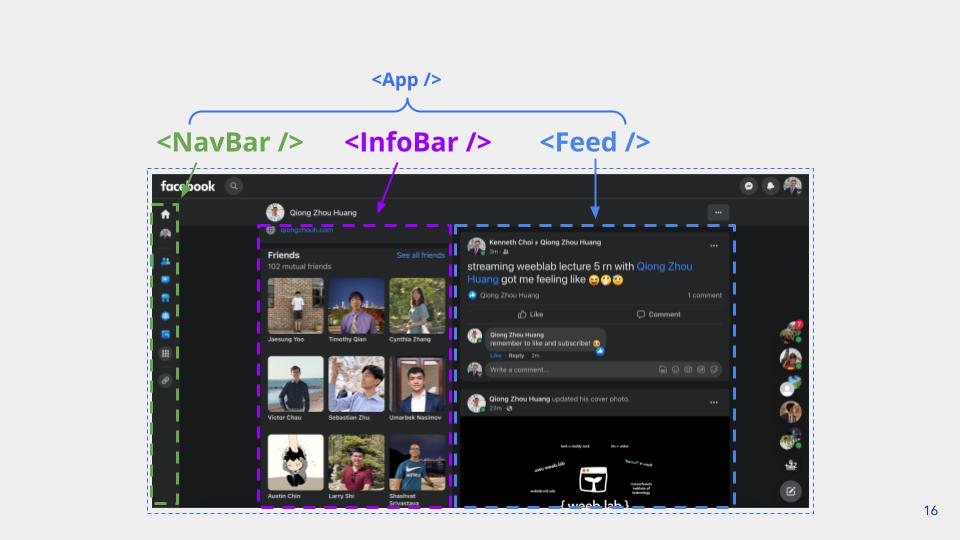
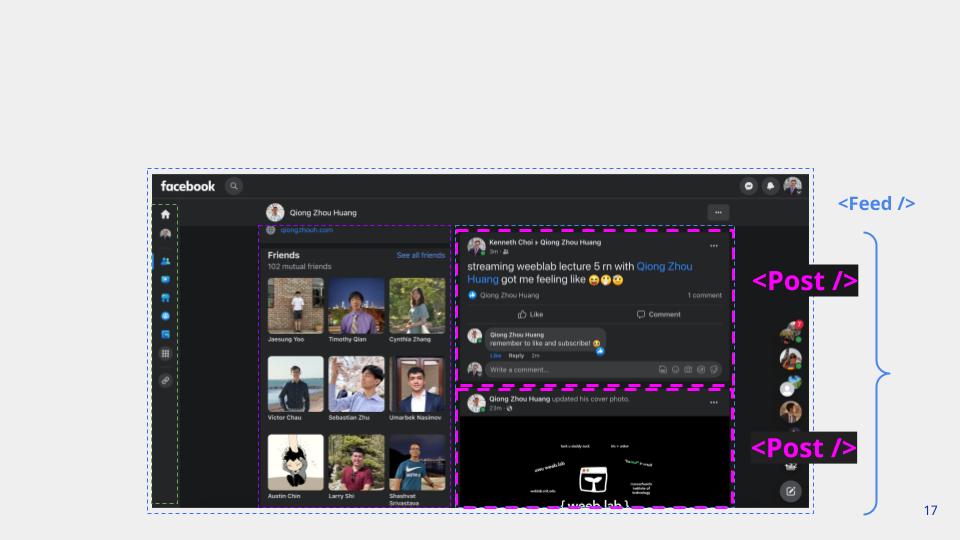
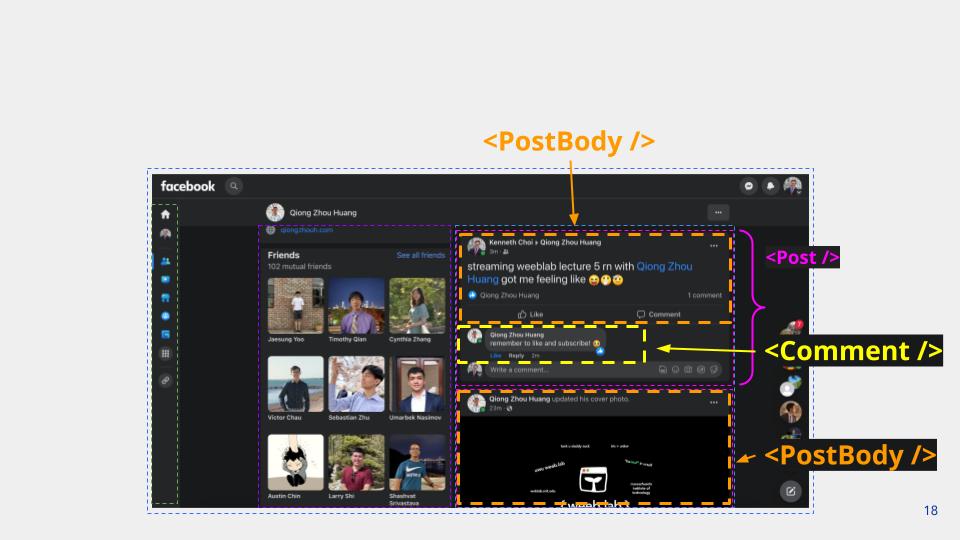
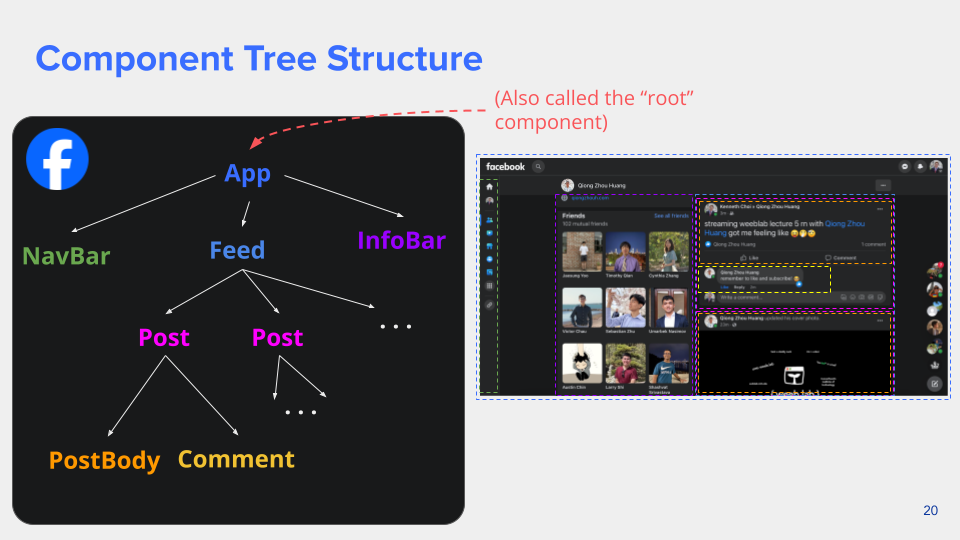
React Apps are composed of components.
Component Tree Structure
Quick Recap
- React is a Framework that lets you divide up your website into reusable components
- Each component is kind of like a “custom HTML tag” that you define
- Components are an abstraction of a bunch of HTML/CSS/Javascript
- The components can be structured into tree hierarchy
Component Structure - Key features of components
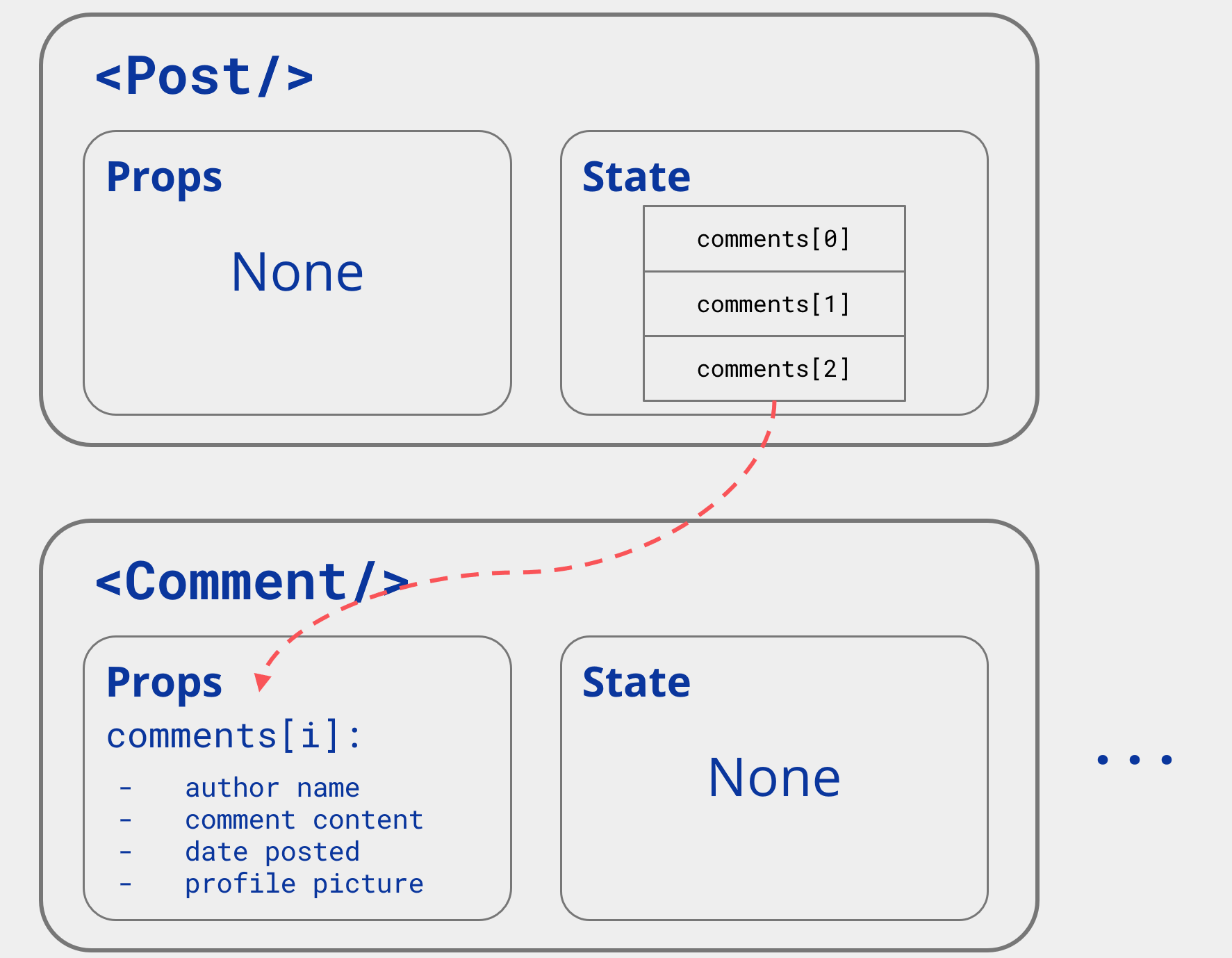
e.g. Comment Component
- This picture describes how the comment is going to be rendered on screen
- It is a “skeleton” or “template” for all comments
Props
Information (inputs) passed down from a parent to a child component
$$ Parent \xrightarrow[]{props} Child $$
e.g. Comment Props
props:
- author name = "Yoda Yuki"
- comment content = "Nogizaka46!"
- date posted = 1 minute ago
- profile picture = yoda.jpgQuick Recap
- Props allow us to create reusable components - renders a skeleton with custom content
- Props are passed in from parent to child ONLY
- Props are immutable
State
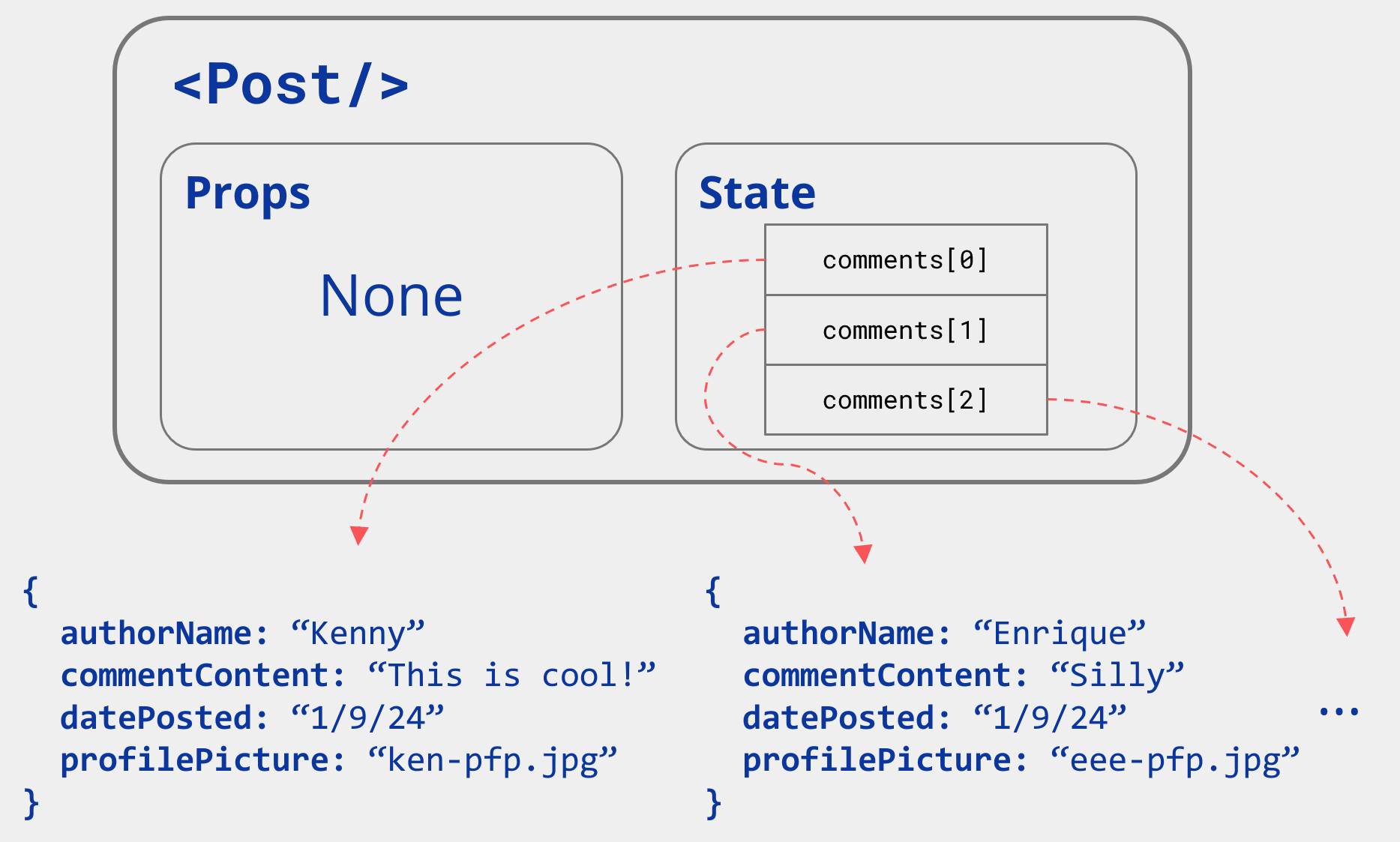
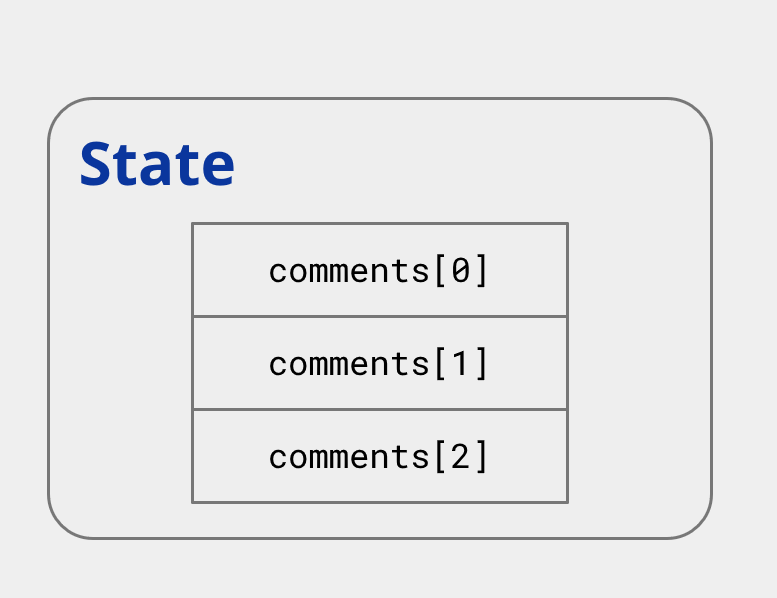
Information maintained by a component
- State let us control what is displayed in th application
- State can be updated (i.e. is mutable unlike props)
- Can be updated by either human inputs (e.g. button clicks) or computer inputs (e.g. network responses)
e.g. Post State
Quick Recap
- State is information maintained by components and lets us control what is displayed in the application
- State is mutable and updated by external inputs
- Can be passed to reusable child components as props
Component Structure Recap
- Components can have props and/or state
- Props are passed down from parent components and are immutable
- State is data maintained by a component and is mutable
- State can be kept in parent components so that it can be passed into reusable child components as props
Coding
import React, { useState } from 'react'; // <- Import React Library
const CommentReply = (props) => { // <- Define Component
return(
)
}
export default CommentReply; //<- Export ComponentThe CommentReply component is a function that takes in props as an input and returns some JSX.
Render
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const CommentReply = (props) => {
return(
<div className="comment-text">
<h5>Yoda Yuki</h5>
<p>Nogizaka46!</p>
</div>
)
}
export default CommentReply; All this hard coding won't make our component reusable.
So we need to use props.
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const CommentReply = (props) => {
return(
<div className="comment-text">
<h5>{props.name}</h5>
<p>{props.content}</p>
</div>
)
}
export default CommentReply; JSX
Stricter version of HTML
Return JSX = what the React component should render
() allows us to write JSX("HTML") code inside JavaScript
{} allows us to return to JavaScript inside the JSX environment to use variables defined inside this React Component
Side-by-side differences: click here
add a State
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const CommentReply = (props) => {
const [isLiked, setIsLiked] = useState(false);
/*
React State syntax:
Initilizes isLiked state to false
Declares setIsLiked as the function to update isLiked
Example:
setIsLiked(true) will set isLiked to true
*/
return(
<div className="comment-text">
<h5>{props.name}</h5>
<p>{props.content}</p>
<p>{isLiked ? "Liked" : "Like"}</p> // Conditionallt render text based on the isLiked State
</div>
)
}
export default CommentReply; Props
Syntax to pass down props
<Post name="Yoda" text="Welcome to Nogizaka!" />name and text are props
Recap
- We divide our app into components, and put one in each file
- Each component is a function with props as the input, and returns JSX (HTML-like code)
- ( ) allows us to enter an JSX environment
- Inside the JSX environment, {} allows us to create a mini JS environment
- We pass in props with
<Post text="I love weblab" /> - We read in those props in the child component with props.text
- We declare state variables with
const [something, setSomething] = useState(initialValue) - React uses className instead of class for css styles



Comments NOTHING